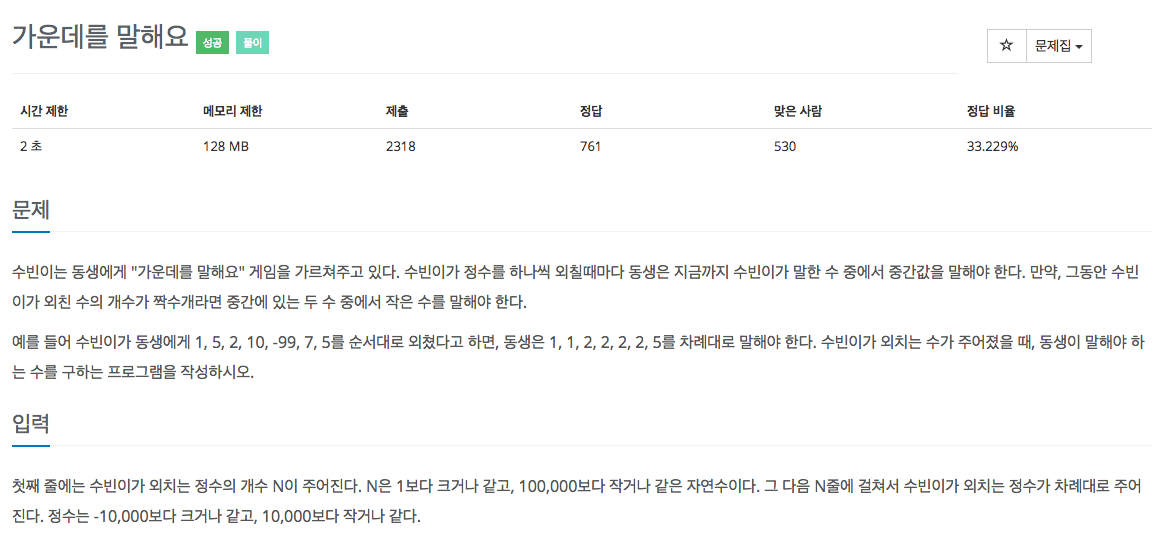
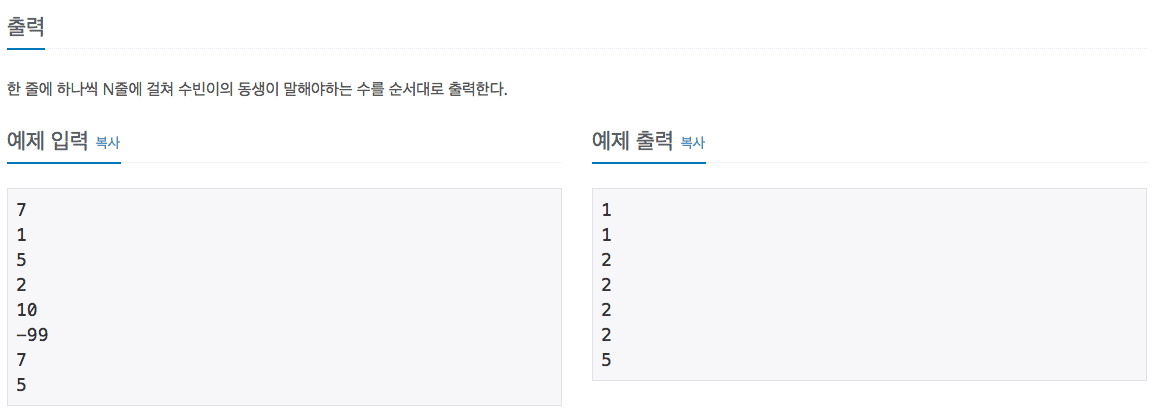
- Problem
- Explain Logic
- [1] Answer Code (18. 02. 19)
- [2] Answer Code (18. 02. 19)
- [3] Wrong Code (18. 02. 19)
Problem
Problem URL : 가운데를 말해요
Explain Logic
알고리즘 분석 :
중간값 구하기 알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
-
Max Heap의 크기는Min Heap의 크기와 같거나, 하나 더 크다. -
Max Heap의 최대 원소는 최소 합의 최소 원소보다 작거나 같다(= 크다).
이 때 알고리즘에 맞지 않다면 Max Heap, Min Heap의 가장 위의 값을 swap해준다.
[결과] 이 때 이 두가지 규칙을 유지해 준다면 항상 Max Heap top값이 중간값이 된다.
보다 자세한 설명이 필요하다면 출처 Blog를 참고하자 !
[1] Answer Code (18. 02. 19)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> max_heap;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> min_heap;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int val;
scanf("%d",&val);
// Formula 1
if(max_heap.size() == min_heap.size())
max_heap.push(val);
else
min_heap.push(val);
// Formula 2
if (!max_heap.empty() && !min_heap.empty() && !(max_heap.top() <= min_heap.top()))
{
int a = max_heap.top();
int b = min_heap.top();
max_heap.pop();
min_heap.pop();
max_heap.push(b);
min_heap.push(a);
}
printf("%d\n", max_heap.top());
}
return 0;
}
Review
-
Oh Ho ~ , 새로운 개념적 접근이다.
-
실생활 프로그램에 유용하게 사용될 알고리즘 같단 생각하에 reSolve 태그를 걸었다.
-
Priority_Queue 개념을 잘못알고 있었다.
-
Root를 기준으로 정렬된 순서로 Node를 갖고 있는지 알았는데
그게 아니라 Root에 Max,Min Value만 갖고 있는것이였다!
[2] Answer Code (18. 02. 19)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int> max_heap,min_heap;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int val;
scanf("%d",&val);
// Formula 1
if(max_heap.size() == min_heap.size())
max_heap.push(val);
else
min_heap.push(-val);
// Formula 2
if (!max_heap.empty() && !min_heap.empty() && !(max_heap.top() <= -min_heap.top()))
{
int a = max_heap.top();
int b = -min_heap.top();
max_heap.pop();
min_heap.pop();
max_heap.push(b);
min_heap.push(-a);
}
printf("%d\n", max_heap.top());
}
return 0;
}
Review
- min_heap에 push할 때
-를 곱하여#include <functional>을 사용하지 않고 구현하였다.
[3] Wrong Code (18. 02. 19)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int v;
scanf("%d",&v);
v1.push_back(v);
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
v2 = v1;
int size = (int) v1.size();
if(! (size & 1)) // size is Even
size--;
printf("%d\n",v1[size>>1]);
v1 = v2;
}
return 0;
}
Review
- 역시나
Priority Queue를 사용하지 않고 풀려고 하니시간 초과