To Do
- STL을 사용하지 않고 자료 구조를 구현해보자.
Stack
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int stack[10001];
int top = -1;
void push(int x){
stack[++top] = x;
}
int empty() {
if( top < 0 )
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void pop() {
if (empty() == 1)
cout << "-1" << "\n";
else {
cout << stack[top] << "\n";
stack[top--] = 0;
}
}
void size(){
cout << top + 1 << "\n";
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
if( s == "push"){
int x;
cin >> x;
push(x);
}
else if ( s == "top") {
if (empty() == 1)
cout << "-1" << "\n";
else
cout << stack[top] << "\n";
}
else if ( s == "pop") {
pop();
}
else if ( s == "empty") {
cout << empty() << "\n";
}
else if ( s == "size") {
size();
}
}
return 0;
}
Queue
const int size = 10;
int queue[size];
int q_front;
int q_rear;
void QueueInit(){
q_front = q_rear = 0;
}
int QueueSize(){
return q_rear - q_front;
}
void QueuePush(int value){
queue[q_rear++ % size] = value;
}
int QueuePop(){
if(q_front == 0)
return -1;
return queue[q_front++];
}
bool QueueEmpty(){
if( q_front == q_rear )
return true;
return false;
}
Tree
typedefstruct node{
int data;
struct node* leftchild;
struct node* rightchild;
};
node* Make_Tree(int key) {
node* Newnode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
Newnode->data = key;
Newnode->leftchild =NULL;
Newnode->rightchild =NULL;
Newnode->leftchild = Make_Tree();
Newnode->rightchild = Make_Tree();
return Newnode;
}
Sort
선택 정렬
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *arr, int a, int b){
int tmp = arr[b];
arr[b] = arr[a];
arr[a] = tmp;
}
void SelectionSort(int *arr, int begin, int end){
for(int i=begin; i<end; i++){
int tmp = i;
for(int j=i+1; j <= end; j++)
if( arr[tmp] > arr[j] )
tmp = j;
if( tmp != i )
swap(arr,i,tmp);
}
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,2,1,4,3};
SelectionSort(arr, 0, 4);
return 0;
}
버블 정렬
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *arr, int a, int b){
int tmp = arr[b];
arr[b] = arr[a];
arr[a] = tmp;
}
void BubbleSort(int *arr, int begin, int end){
for(int i=end; i>begin; i--){
for(int j=begin; j<i; j++)
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1])
swap(arr, j, j+1);
}
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,2,1,4,3};
BubbleSort(arr, 0, 4);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
cout << arr[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
삽입 정렬
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *arr, int a, int b){
int tmp = arr[b];
arr[b] = arr[a];
arr[a] = tmp;
}
void InsertSort2(int *arr, int begin, int end){
for(int i=begin+1; i<=end; i++){
int j;
int v = arr[i];
for(j=i; j>begin && arr[j-1] > v; j--)
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
if( i != j)
arr[j] = v;
}
}
void InsertSort(int *arr, int begin, int end){
for(int i=0; i<end; i++){
for(int j=i+1; j>=0; j--){
if( arr[j-1] > arr[j])
swap(arr, j-1, j);
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,2,1,4,3};
InsertSort(arr, 0, 4);
return 0;
}
퀵 정렬
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *arr, int a, int b){
int tmp = arr[b];
arr[b] = arr[a];
arr[a] = tmp;
}
void QuickSort(int *arr, int begin, int end){
int pivot = begin;
int left = begin;
int right = end;
while (left < right) {
while (arr[left] <= arr[pivot] && left < end)
left += 1;
while (arr[right] >= arr[pivot] && right > begin)
right -= 1;
if( left < right ){
swap(arr, left, right);
continue;
}
swap(arr, pivot, right);
QuickSort(arr, begin, right-1);
QuickSort(arr, right+1, end);
}
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,2,1,4,3};
QuickSort(arr, 0, 4);
return 0;
}
합병 정렬
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void MergeArray(int *arr, int *copy, int start, int end){
int mid = (start + end ) >> 1;
int i = start;
int j = mid+1;
int k = start;
while (i <= mid && j <= end) {
if( arr[i] <= arr[j])
copy[k++] = arr[i++];
else
copy[k++] = arr[j++];
}
while (i <= mid)
copy[k++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= end)
copy[k++] = arr[j++];
for(int i=start; i<=end; i++)
arr[i] = copy[i];
}
void MergeSort(int *arr, int *copy, int start, int end){
if(start == end)
return ;
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
MergeSort(arr, copy, start, mid);
MergeSort(arr, copy, mid+1, end);
MergeArray(arr, copy, start, end);
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,1,4,3,2};
int arr2[5];
MergeSort(arr, arr2, 0, 4);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
cout << arr2[i] << endl;
}
-
합병 정렬은 O(NlogN)이기 때문에 성능이 준수하다.
-
다만 30개 이하의 숫자를 정렬할 때는 삽입 정렬과 별 차이가 없고 정렬하는데 추가적인 메모리가 필요하다는 단점이 있다.
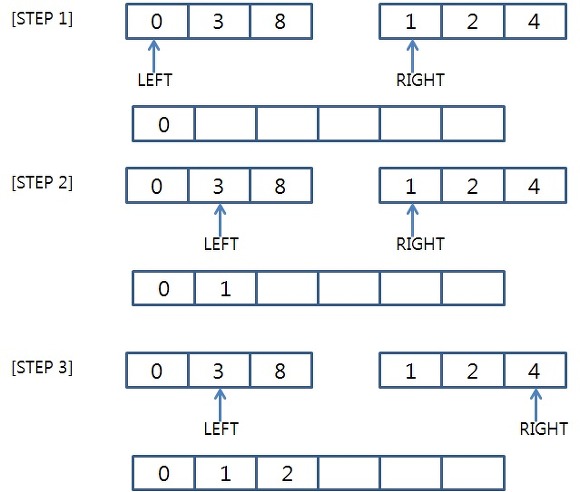
-
보통은 재귀 함수를 사용해서 만든다.
-
합병 정렬은 분할 정복 알고리즘에 속한다.
-
유명한 수학자 폰 노이만이 개발했다.
-
합병 정렬은 배열을 두 개로 나누고, 나눈 것을 다시 두 개로 계속 나눠 정렬한다.
-
합병 정렬의 단점은 array 외에도 result라는 추가적인 저장 공간이 필요하다는 것이다.
-
그래서 메인 메모리의 반이상의 배열 크기를 갖는다면 메인 메모리 내에서 사용할 수 없다.
-
외부 정렬 방식의 하나이다.
외부 정렬이란?
데이터의 크기가 주기억장소보다 클 경우 외부 기억장치(디스크, 테이프 등)을 사용하여 정렬하는 방식이다. -
참고로 일부 브라우저에서는 배열.sort()를 할 때 합병 정렬을 사용한다고한다.
힙 정렬
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *arr, int a, int b){
int tmp = arr[b];
arr[b] = arr[a];
arr[a] = tmp;
}
void Heapify(int*arr, int index, int size) {
for (int ch = (index << 1) | 1; ch <size; index = ch, ch = ch << 1 | 1) {
if (ch + 1<size&& arr[ch + 1] > arr[ch])
++ch;
if (arr[ch] <= arr[index])
return;
swap(arr,ch, index);
}
}
void HeapSort(int*arr, int begin, int end) {
int *base = arr + begin;
int size = end - begin + 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
Heapify(base, i, size);
while (--size >= 1) {
swap(arr,0, size);
Heapify(base, 0, size);
}
}
int main(){
int arr[5] = {5,2,1,4,3};
HeapSort(arr, 0, 4);
return 0;
}
바이너리 서치(Binary Search)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
BS function return target index
*/
int BS(int *arr, int _end, int target){
int st = 0;
int end = _end;
int mid;
while (st <= end) {
mid = ( st + end ) >> 1;
if( target == arr[mid] )
return mid;
else if( target > arr[mid] )
st = mid + 1;
else
end = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
// arr은 정렬된 상태여야 한다.
int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
printf("%d\n", BS(arr, 4, 2)); // 1
printf("%d\n", BS(arr, 4, 6)); // -1
printf("%d\n", BS(arr, 4, 4)); // 3
}