이 글의 코드 및 정보들은 강의를 들으며 정리한 내용을 토대로 작성하였습니다.
Goal
-
Spring Boot 환경에서
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 클래스의 다양한 역할 중
Convert와 Formatter를 등록하는 과정에 대해 알아보자.
Where to use
WebConfig
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
}
-
일반적으로 WebConfig 파일에서 Web과 관련된 설정을 한다.
-
여기서 WebMvcConfigurer의 구현체가 바로 WebMvcAutoConfiguration이다.
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 클래스에서
Convert와 Formatter가 어떻게 등록하는지 알아보자.
WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter.class –> addFormatters( )
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
// Step into addBeans() !!!
ApplicationConversionService.addBeans(registry, this.beanFactory);
}
ApplicationConversionService.class –> addBeans( )
public static void addBeans(FormatterRegistry registry, ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Set<Object> beans = new LinkedHashSet<>();
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(GenericConverter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Converter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Printer.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Parser.class).values());
for (Object bean : beans) {
if (bean instanceof GenericConverter) {
registry.addConverter((GenericConverter) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Converter) {
registry.addConverter((Converter<?, ?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Formatter) {
registry.addFormatter((Formatter<?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Printer) {
registry.addPrinter((Printer<?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Parser) {
registry.addParser((Parser<?>) bean);
}
}
}
-
addBeans() 메소드를 보면
GenericConverter / Converter / Printer / Parser 타입의 빈을
등록해주는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Q. 그런데 Formatter는 어떻게 등록되는거지?
-
addBeans( ) 메소드안에서
볼 수 있는 4개의 타입에 Formatter는 보이지 않는다.
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(GenericConverter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Converter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Printer.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Parser.class).values());
-
그래서 하나하나 상속 구조를 살펴보니
Printer와 Parser 클래스를
Formatter가 상속하는 구조였다.
// Printer : 객체를 문자열로 어떻게 보여줄지 명시
// Parser : 문자열을 객체로 어떻게 변환 활 것인가를 명시
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {
}
Example Code
Config
Spring MVC
WebConfig
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addFormatter(new PersonFormatter());
registry.addConverter(new PersonConverter.StringToPersonConverter());
registry.addConverter(new PersonConverter.PersonToStringConvert());
}
}
-
Spring MVC 환경에서는
직접 Formatter와 Converter를 등록해줘야한다.
Spring Boot
WebConfig
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
// registry.addFormatter(new PersonFormatter());
// registry.addConverter(new PersonConverter.StringToPersonConverter());
// registry.addConverter(new PersonConverter.PersonToStringConvert());
}
}
-
WebConfig를 다음과 같이 수정한다.
-
Spring Boot 환경에서는
Converter / Formatter 클래스를 만들고
Bean 선언만 해주면 알아서 등록이 된다.
-
그렇기 때문에 WebConfig와 같은
Configuration에 Bean을 등록 할 필요가 없어진다.
-
Bean을 등록해주는 과정은
위에서 언급했던 ApplicationConversionService.class –> addBeans()에서 이뤄진다.
-
이와 관련된 검증은 Example을 통해 확인해본다.
Domain
Person
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Person {
private String name;
}
Converter
PersonConverter
public class PersonConverter {
@Component
public static class StringToPersonConverter implements Converter<String, Person> {
@Override
public Person convert(String s) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(s);
return person;
}
}
@Component
public static class PersonToStringConvert implements Converter<Person, String> {
@Override
public String convert(Person person) {
return person.getName();
}
}
}
주의 사항
-
static 키워드를 반드시 붙혀줘야한다.
-
그렇지 않으면 등록이 되지 않는다.
-
잘못된 사용 : public class PersonToStringConvert
-
올바른 사용 : public static class PersonToStringConvert
-
Formatter
PersonFormatter
@Component
public class PersonFormatter implements Formatter<Person> {
@Override
public Person parse(String s, Locale locale) throws ParseException {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(s);
return person;
}
@Override
public String print(Person person, Locale locale) {
return person.toString();
}
}
Controller
EventController
@RestController
public class EventController {
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public String events(@PathVariable("name") Person person){
return "hello " + person.getName();
}
}
Test Code
EventControllerTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class EventControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/hello/goodgid"))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(content().string("hello goodgid"));
}
}
-
Spring Boot 환경에서 Test를 진행한다.
-
TC를 실행시키고
ApplicationConversionService에
Break Point를 걸고 Debug를 해본다.
ApplicationConversionService.class –> addBeans()
public static void addBeans(FormatterRegistry registry, ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Set<Object> beans = new LinkedHashSet<>();
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(GenericConverter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Converter.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Printer.class).values());
beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Parser.class).values());
for (Object bean : beans) {
if (bean instanceof GenericConverter) {
registry.addConverter((GenericConverter) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Converter) {
registry.addConverter((Converter<?, ?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Formatter) {
registry.addFormatter((Formatter<?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Printer) {
registry.addPrinter((Printer<?>) bean);
}
else if (bean instanceof Parser) {
registry.addParser((Parser<?>) bean);
}
}
}
-
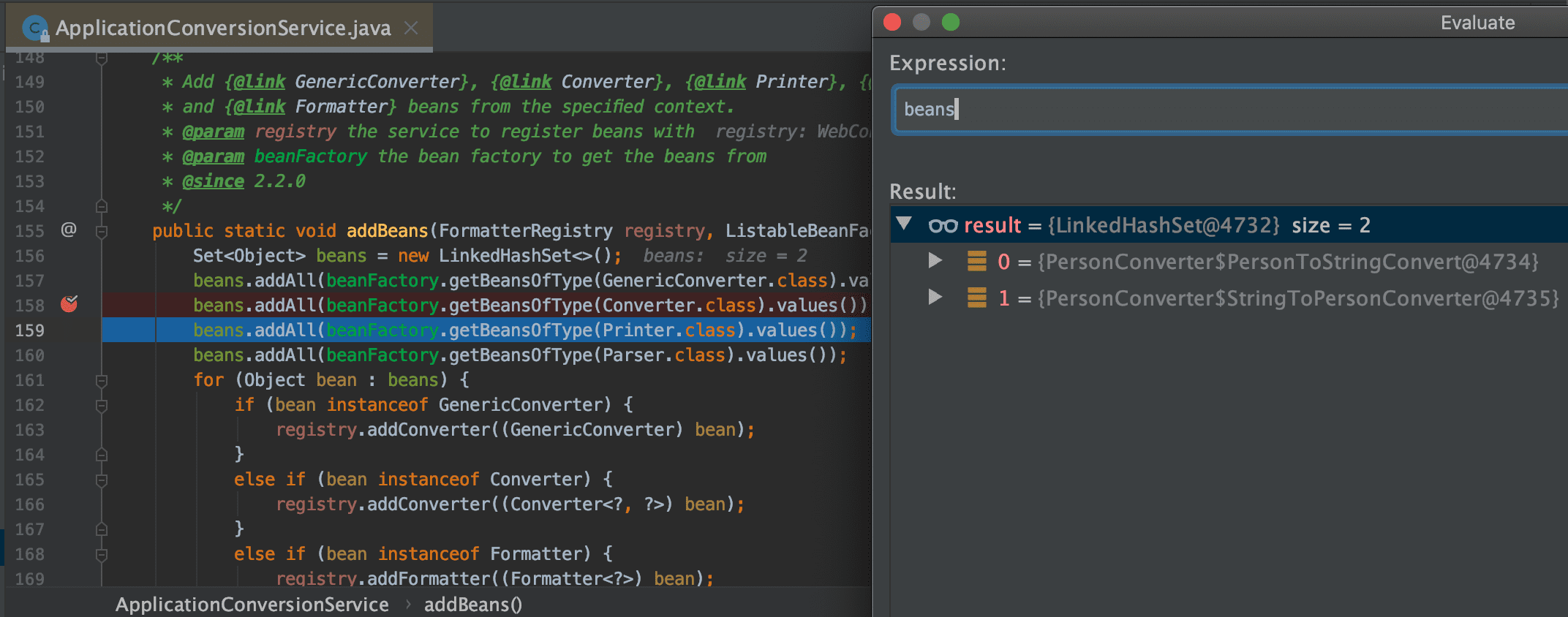
[158] : beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Converter.class).values( )) 코드를 지나면
2개가 등록된다.
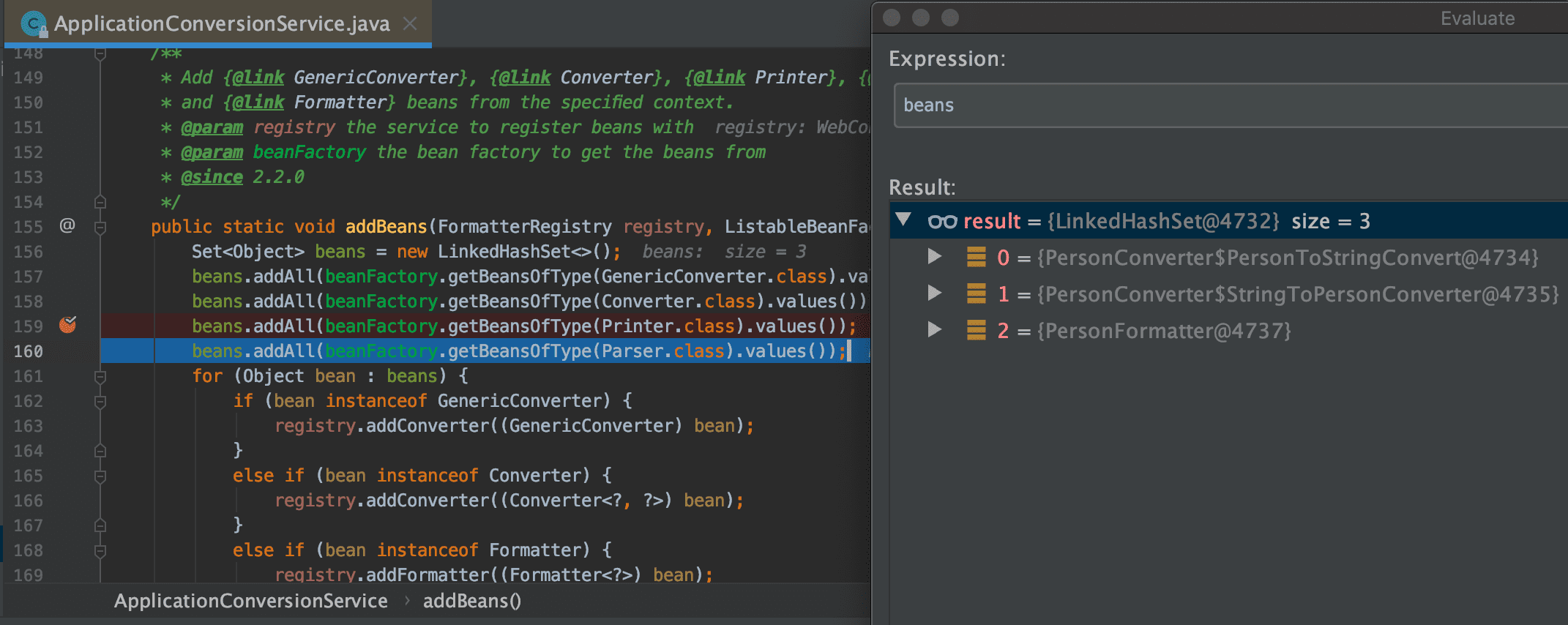
-
[159] : beans.addAll(beanFactory.getBeansOfType(Printer.class).values( )) 코드를 지나면
1개가 등록된다.
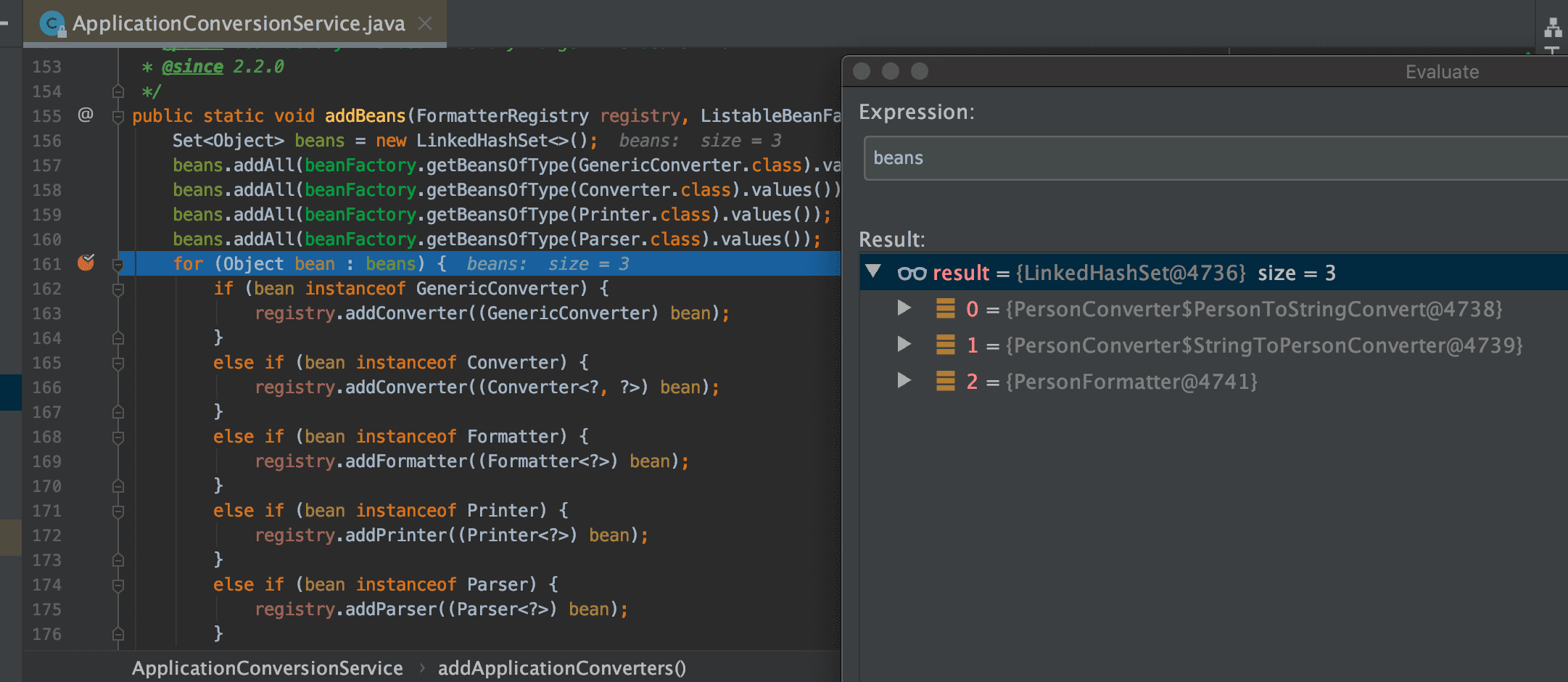
-
그래서 최종적으로는
3개가 등록되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Summary
-
Spring Boot 환경에서
Converter와 Formatter를
Bean 선언만 하여도
자동적으로 등록이 되는 원리에 대해 알아봤다.
-
끝으로 동영상을 보면서
이번글을 복습해보자.
-
추가적으로
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 클래스는
Spring Boot 환경에서
@SpringBootApplication 어노테이션과 밀접한 관련이 있다.
-
그것과 관련된 내용은 다음 글을 참고하자.