꾸준함이 실력입니다.
One Two be super Developer-
LeetCode : 344. Reverse String
(Easy) Reverse String
Problem
Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters char[]. Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory. You may assume all the characters consist of printable ascii characters.
Example
Input: ["h","e","l","l","o"] Output: ["o","l","l","e","h"]
Code (20. 11. 11) (x)
public void reverseString(char[] s) { int length = s.length; char[] ans = new char[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { ans[i] = s[length - 1 - i]; } for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { s[i] = ans[i]; } }-
막 풀어도 될까 했는데 풀리는구나.
그래도 좋은 코드 참고하자.
-
-
LeetCode : 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Problem
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], 3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
Code (20. 11. 11)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { return find(0, root); } public int find(int depth, TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return depth; } return Math.max(find(depth + 1, node.left), find(depth + 1, node.right)); }-
머리 아팠다.
오랜만에 재귀로 푸려니까 너무 어려웠다.
Code (21. 07. 14)
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } return getMaxDepth(root, 1); } public int getMaxDepth(TreeNode node, int ans) { if (node == null) { return ans; } int leftMaxDepth = 0; int rightMaxDepth = 0; if (node.left != null) { leftMaxDepth = getMaxDepth(node.left, ans + 1); System.out.println("leftMaxDepth : " + leftMaxDepth); } if (node.right != null) { rightMaxDepth = getMaxDepth(node.right, ans + 1); System.out.println("rightMaxDepth : " + rightMaxDepth); } ans = Math.max(ans, Math.max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth)); return ans; } }-
LeetCode 웹 IDE에서 바로 풀었다.
풀 수 있을까? 했는데 두드려보니 풀렸다.
Code (21. 09. 19) (x)
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { return go(root,0,0); } private int go(TreeNode node, int depth, int ans) { if (node == null) { return depth; } ans = Math.max(ans, go(node.left, depth+1, ans)); ans = Math.max(ans, go(node.right, depth+1, ans)); return ans; } }- 다시 풀 필요 X
Reference
-
-
Google Adsense : $100를 돌파하다.
Google Adsense
- Google Adsense의 수익금 $100를 돌파했다.
$100 달성
-
Google Adsense Home에 들어가니
다음과 같은 화면이 나를 반겼다.
바로 업데이트 버튼을 눌렀다.
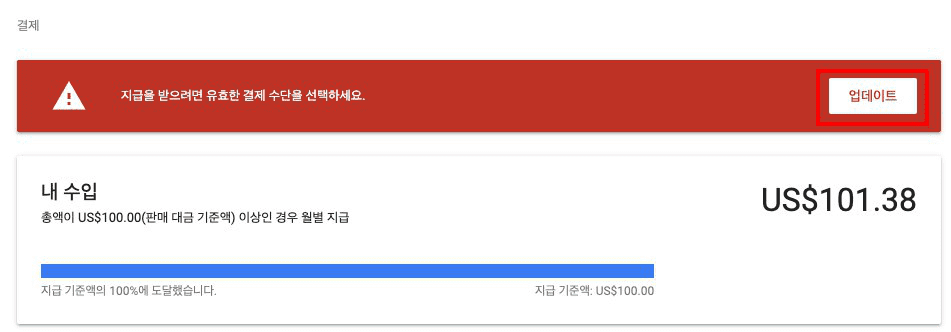
- 업데이트 버튼을 누르면 다음과 같은 화면이 보인다.

-
Google Adsense 가입 시
결제 수단을 설정하지 않았기 때문에 설정을 해준다.
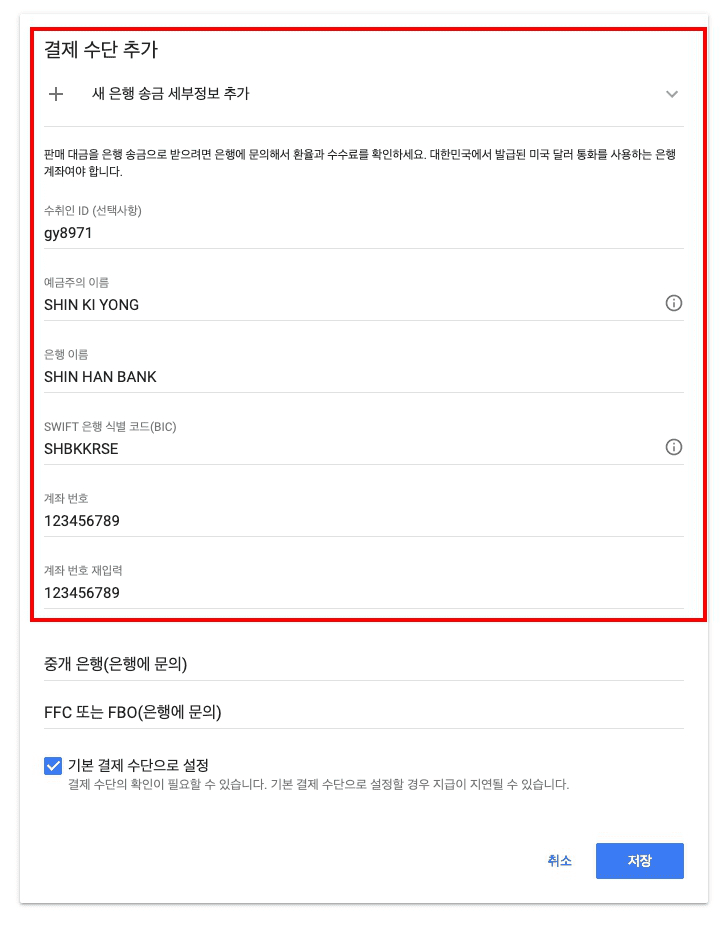
- 정상적으로 등록되었고 이제 저 계좌로 돈이 들어오는 걸 기다리면 된다.
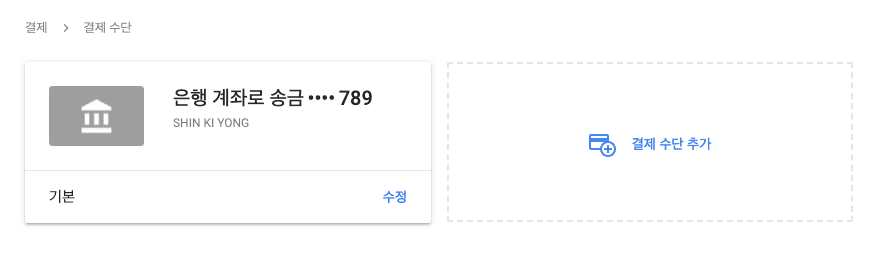
-
Spring Boot SQL Option : 'show_sql' Option Deep 하게 알아보기
-
LeetCode : 7. Reverse Integer
(Easy) Reverse Integer
Problem
Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer. Note: Assume we are dealing with an environment that could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 0 when the reversed integer overflows.
Example
Input: x = 123 Output: 321
Code (20. 11. 08)
public int reverse(int x) { if (x == 0) { return 0; } while (true) { if (x % 10 == 0) { x /= 10; } else { break; } } StringBuilder answer = new StringBuilder(); if (x < 0) { answer.append("-"); x *= -1; } while (x != 0) { answer.append(x % 10); x /= 10; } int ans; try { ans = Integer.parseInt(answer.toString()); } catch (Exception e){ return 0; } return ans; }
Feed Back
Case 1
class Solution { public int reverse(int x) { long num = 0; while (x != 0) { num = num * 10 + x % 10; x = x / 10; } if (num != (int) num) { return 0; } return (int) num; } }- long으로 계산하고 int로 변환한다는 아이디어가 좋았다.
-
Spring Boot SQL Option 알아보기 :: show_sql, format_sql, use_sql_comments, org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql
SQL Option
SQL 보기
-
Hibernate가 DB에 날리는 모든 Query를 보여준다.
-
해당 옵션과 관련해서는 반드시 알아야 할 부분이 있다.
그 부분에 대해서는 Spring Boot SQL Option : ‘show_sql’ Option Deep 하게 알아보기 글을 참고하자.
application.yml
spring: jpa: properties: hibernate: show_sql: trueapplication.properties
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql = trueOutput
Hibernate: select testentity0_.id as id1_8_0_ from test_entity testentity0_ where testentity0_.id=? Hibernate: insert into test_entity (id) values (?)
-
Recent Posts
- Cursor가 매일 수십억 건의 AI 코드 완성을 처리하는 방식
- A 레코드와 CNAME 레코드는 뭐가 다른걸까?
- 분산 시스템에서 순서가 보장되지 않은 이벤트를 다루는 전략
- DU(Disk Usage) 명령어를 아시나요?
- 2PC(Two-Phase Commit)란 무엇일까?
- DIG(Domain Information Groper) 명령어를 아시나요?
- 샤딩과 파티셔닝, 그 차이에 대하여
- LeetCode : 692. Top K Frequent Words
- Redis 서버에 접속중인 Client 목록 확인 방법
- LeetCode : 1299. Replace Elements with Greatest Element on Right Side
Categories
- Conference 11
- AlgorithmSkill 39
- DB 24
- Algorithm 175
- Crawling 1
- Node.js 15
- Linux 6
- AWS 11
- E.T.C 51
- Competition 5
- Python 26
- BlockChain 36
- MachineLearning 19
- 파일처리 14
- OS 12
- Server 31
- Docker 1
- Web 1
- JavaScript 18
- Network 39
- Git 6
- Technology 64
- DataStructure 1
- C/C++ 1
- HTTP 14
- Java 38
- Redis 9
- Retrospective 7
- Spring 72
- SpringBoot 16
- Kafka 26
- CleanCode 12
- TIL 4
- Blog 7
- Nginx 6
- MyBatis 6
- Regex 4
- EffectiveJava 2
- Spock 1
- Junit5 4
- Intellij 1
- CLI 1
- LeetCode 203
- MySQL 1
- JavaOptimizing 6
- Feign 1
- Karate 2
- Github 8
- SystemDesign 23
- Gradle 3
- Logback 3
- Kotlin 7
- CleanArchitecture 6
- Tech 6