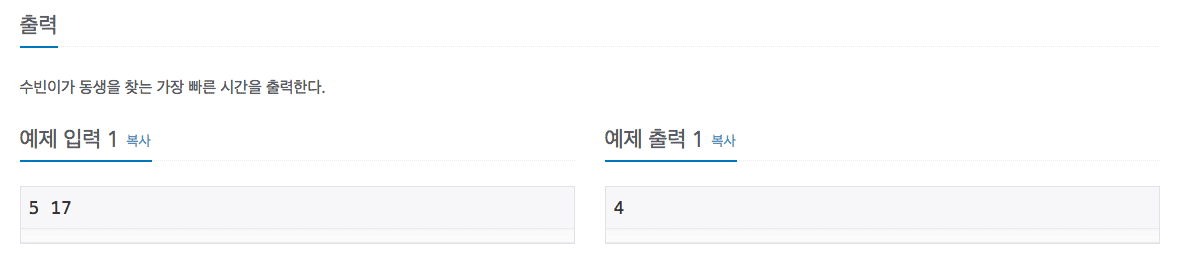
Problem
Problem URL : 숨바꼭질
[1] Answer Code (18. 09. 21)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int visit[100001];
int main(){
int st,dest;
cin >> st >> dest;
queue<int> q;
q.push(st);
int time = -1;
int flag = 0;
while (! q.empty()) {
if( flag )
break;
time ++;
int size = (int) q.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
int top = q.front();
q.pop();
if( top == dest ){
flag = 1;
break;
}
if( visit[top] ) // Already Visit
continue;
visit[top] = 1;
if( top - 1 >= 0 && !visit[top - 1] ) // Already Visit
q.push(top - 1);
if(top + 1 <= 100000 && !visit[top + 1] ) // Already Visit
q.push(top + 1);
if(top * 2 <= 100000 && !visit[top * 2] ) // Already Visit
q.push(top * 2);
} // end of for i
} // end of while
if( flag )
cout << time << endl;
return 0;
}
Review
-
너무 성급하게 풀려고 했더니 잔실수가 너무 많이 생겼다.
-
Before처럼 했을 시 문제가 발생한다.
// Before
while (! q.empty()) {
if( flag ){
cout << time << endl;
break;
}
...
}
/*
큐에 1개 값이 있고
그 값이
for 안에
int top = q.front();
q.pop();
코드 이후
if( top == dest )
조건을 충족시키면
for은 Break된다.
그러면 이 때 큐는 Empty가 되고
다시 while loop를 돌 땐
큐가 Empty이기 때문에
if( flag ){
cout << time << endl;
break;
}
위 코드를 수행할 수 가 없어
틀리는 문제가 발생하였다.
*/
// After
if( flag ){
cout << time << endl;
}
[2] Answer Code (18. 09. 23)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define p pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
int v[100001]; // v is visit
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int st, dest;
cin >> st >> dest;
queue<p> q;
q.push({st,0});
v[st] = 1;
while (! q.empty()) {
int top = q.front().first;
int time = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(top == dest){
cout << time << endl;
break;
}
if( top + 1 < 100001 && !v[top+1] ){
v[top+1] = 1;
q.push({top+1, time+1});
}
if( top - 1 > -1 && !v[top-1]){
v[top-1] = 1;
q.push({top-1, time+1});
}
if( top * 2 < 100001 && !v[top*2]){
v[top*2] = 1;
q.push({top*2, time+1});
}
}
return 0;
}
Review
-
Tree 구조로 생각해서 푸니까 명료하게 로직을 짤 수 있었다.
-
같은 레벨에 대해서는 중복처리를 해줘도 된다.
시작점이 1 이라면
0 2 2 로 갈 수 있다.
이럴 경우 2 2 같은 경우는 같은 경우의 수를 보이게 된다.
그렇기 때문에 queue에 push하면서
동시에 visit 체크를 통해
같은 레벨에 대해 같은 값이 queue에 push되는 수를 제거 했다.
다시말하면
1
0 2(1) 2(2) 일 것이다.
이때 2(1)이 push되면
같은 레벨에 있는 2(2)같은 경우는 queue에 push가 될 필요가 없다.
- 같은 레벨이 아니라 다른 레벨인데 값이 같을 경우 단순히 값만으로 visit을 체크하면 최적이 아닐 수 있지 않을까?
예를 들어보자
문제의 규칙을 따르면
1 2 3 2 // [1]
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 6 과 같이 움직일 수 있다.
이 때 [1] 경우에 가장 마지막에 2를 push하기 위한 조건은
이전에 2위치를 visit하지 않았을 경우다.
그런데 이전에 2를 visit을 했다면
현재 push할 2는 절대로
이전에 2보다 적은 값을 갖고 있을 수 없다.
Tree 구조로 생각해보면
같은 값이더라도
레벨이 더 낮은 값이 레벨이 더 높은 값보다
무조건 Depth가 낮기 때문이다.
level 0 : 1
level 1 : 0 2 2
level 2 : 1 3 4
level 3 : 2 4 6